Share & grow the world's knowledge!
We want to connect the people who have knowledge to the people who need it, to bring together people with different perspectives so they can understand each other better, and to empower everyone to share their knowledge.
Write a Python class named Circle constructed by a radius …
class Circle(): def __init__(cir, r): cir.radius = r def area(cir): return cir.radius**2*3.14 def perimeter(cir): return 2*cir.radius*3.14 NewCircle = Circle(8) print("Area : ",NewCircle.area()) print("Perimeter : ",NewCircle.perimeter())
class Circle(): def __init__(cir, r): cir.radius = r def area(cir): return cir.radius**2*3.14 def perimeter(cir): return 2*cir.radius*3.14 NewCircle = Circle(8) print("Area : ",NewCircle.area()) print("Perimeter : ",NewCircle.perimeter())See lessForward engineering is not necessary if an existing software product …
Q1.Forward engineering is not necessary if an existing software product is producing the correct output. Is the statement true or not. Justify with your answer. Answer: No, It's not true. As Forward Engineering is a method of creating or making an application with the help of the given requirements.Read more
Q1.Forward engineering is not necessary if an existing software product is producing the correct output. Is the statement true or not. Justify with your answer.
Answer:
No, It’s not true. As Forward Engineering is a method of creating or making an application with the help of the given requirements. Forward engineering is also known as Renovation and Reclamation. Forward engineering is a technique of creating high-level models or designs to make in complexities and low-level information. Therefore this kind of engineering has completely different principles in numerous package and information processes. Forward Engineering applies of all the software engineering process which contains SDLC to recreate associate existing application. It is near to full fill new needs of the users into re-engineering. Forward engineering deals with the conversion of business processes, services, and functions into applications. In this method business model is developed first. Then, a top-to-down approach is followed to urge the package from the model developed.
Q2.List and explain different types of testing done during the testing phase.
Answer:
Accessibility Testing
Accessibility testing is the practice of ensuring your mobile and web apps are working and usable for users without and with disabilities such as vision impairment, hearing disabilities, and other physical or cognitive conditions.
Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing ensures that the end-user (customers) can achieve the goals set in the business requirements, which determines whether the software is acceptable for delivery or not. It is also known as user acceptance testing (UAT).
Black Box Testing
Black box testing involves testing against a system where the code and paths are invisible.
End to End Testing
End to end testing is a technique that tests the application’s workflow from beginning to end to make sure everything functions as expected.
Functional Testing
Functional testing checks an application, website, or system to ensure it’s doing exactly what it’s supposed to be doing.
Interactive Testing
Also known as manual testing, interactive testing enables testers to create and facilitate manual tests for those who do not use automation and collect results from external tests.
Integration Testing
Integration testing ensures that an entire, integrated system meets a set of requirements. It is performed in an integrated hardware and software environment to ensure that the entire system functions properly.
See lessEnlist the Technical Features of Pentium?
Features of Pentium Processor are as follows: Superscalar architecture Separate data and instruction caches Bus cycle pipelining Execution tracing 64-bit data bus Internal parity checking Dynamic branch prediction Dual processing support 256 lines between instruction cache and prefetch buffers; alloRead more
Features of Pentium Processor are as follows:
- Superscalar architecture
- Separate data and instruction caches
- Bus cycle pipelining
- Execution tracing
- 64-bit data bus
- Internal parity checking
- Dynamic branch prediction
- Dual processing support
- 256 lines between instruction cache and prefetch buffers; allows 32 bytes to be transferred from cache to buffer
- Data cache
- 8 KB dedicate data cache gives data to execution units
- 32 byte lines
- Two parallel integer execution units
- Allows the execution of two instructions to be executed simultaneously in a single processor clock
- Floating point unit
- It includes
- Faster internal operations
- Local advanced programmable interrupt controller
- Speeds up upto 5 times for common operations including add, multiply and load, than 80486
- Branch Prediction Logic
- To reduce the time required for a branch caused by internal delays
- When a branch instruction is encountered, microprocessor begins prefetch instruction at the branch address
- Data Integrity and Error Detection
- Has significant error detection and data integrity capability
- Data parity checking is done on byte – byte basis
- Address parity checking and internal parity checking features are added
- Dual Integer Processor
- Allows execution of two instructions per clock cycle
- The other two (U pipe and V pipe) execute integer instructions
- Parallel execution of several instructions – superscalar processor
See lessHow do READY, INTR and NMI Works in Microprocessor?
(i)READY: This is the acknowledgement from the memory or slow device that they have completed the data transfer. The signal made available by the devices is synchronized by the 8284A clock generator to provide ready input to the microprocessor. The signal is active high(1). (ii)INTR: The INTRRead more
(i)READY:
This is the acknowledgement from the memory or slow device that they have completed the data transfer. The signal made available by the devices is synchronized by the 8284A clock generator to provide ready input to the microprocessor. The signal is active high(1).
(ii)INTR:
The INTR is a maskable interrupt because the microprocessor will be interrupted only if interrupts are enabled using set interrupt flag instruction. It should not be enabled using clear interrupt Flag instruction.
The INTR interrupt is activated by an I/O port. If the interrupt is enabled and NMI is disabled, then the microprocessor first completes the current execution and sends ‘0’ on INTA pin twice. The first ‘0’ means INTA informs the external device to get ready and during the second ‘0’ the microprocessor receives the 8 bit, say X, from the programmable interrupt controller.
These actions are taken by the microprocessor −
(iii)NMI:
It is a single non-maskable interrupt pin (NMI) having higher priority than the maskable interrupt request pin (INTR)and it is of type 2 interrupt.
When this interrupt is activated, these actions take place −
- Completes the current instruction that is in progress.
- Pushes the Flag register values on to the stack.
- Pushes the CS (code segment) value and IP (instruction pointer) value of the return address on to the stack.
- IP is loaded from the contents of the word location 00008H.
- CS is loaded from the contents of the next word location 0000AH.
- Interrupt flag and trap flag are reset to 0.
See lessCreate a network that implement the FTP server
Search your question in the search box provided on the homepage before asking it on the website. or Directly search questions on Google with the word 'Sikshapath' added to the last. Example: 'create a network that implement the ftp server sikshapath'
Search your question in the search box provided on the homepage before asking it on the website.
or
Directly search questions on Google with the word ‘Sikshapath’ added to the last.
Example: ‘create a network that implement the ftp server sikshapath’
See less(CYCLOMATIC/MCCABE COMPLEXITY) Consider the following bubblesort sorting algorithm: procedure bubbleSort( …
Answers: (a) Flowchart: (b) Calculation of cyclomatic complexity Cyclomatic Complexity, M = E - N + 2P Where, E = no of edges N = no of nodes P = no of connected components Excluded the START and the END node; and corresponding edges N = 5 E = 6 P = 1 2P = 2*1= 2 Cyclomatic Complexity, M = 6 - 5 + 2Read more
Answers:
(a) Flowchart: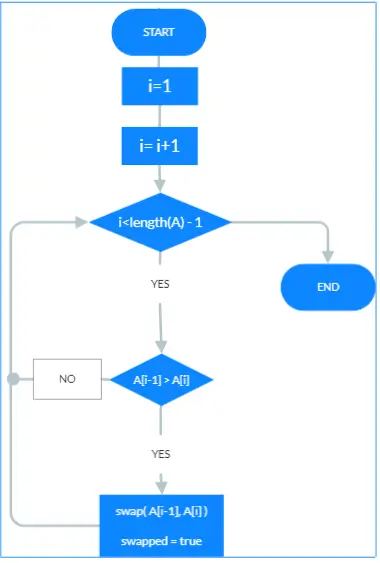
(b) Calculation of cyclomatic complexity
Cyclomatic Complexity, M = E – N + 2P
Where, E = no of edges N = no of nodes P = no of connected components
Excluded the START and the END node; and corresponding edges N = 5 E = 6 P = 1
2P = 2*1= 2
Cyclomatic Complexity, M = 6 – 5 + 2 = 3
See lessA mathematical-model with a collection of operations defined on that model is called
Correct Option is (d) Abstract Data Type
Correct Option is (d) Abstract Data Type
See lessWhich data structure is used for implementing recursion?
Correct Option is (c.) Stack .
Correct Option is (c.) Stack .
See lessSoftware Maintenance is costlier” Justify the statement Give some design …
Q1.Software Maintenance is costlier” Justify the statement Answer: Reports suggest that the cost of maintenance is high. A study on estimating software maintenance found that the cost of maintenance is as high as 67% of the cost of entire software process cycle. On an average, the cost of software mRead more
Q1.Software Maintenance is costlier” Justify the statement
Answer:
Reports suggest that the cost of maintenance is high. A study on estimating software maintenance found that the cost of maintenance is as high as 67% of the cost of entire software process cycle.
On an average, the cost of software maintenance is more than 50% of all SDLC phases. There are various factors, which trigger maintenance cost go high, such as:
Real-world factors affecting Maintenance Cost
Software-end factors affecting Maintenance Cost
Q2.Give some design principles for maintainability.
Answer:
Design Principles in Software Engineering:
These principles relate to how you develop the design for a system, how you implement specific components, and how you should write your code.
1. Divide and Conquer
One of the core principles in any problem-solving situation, including system design, is divide and conquer. It means breaking a problem into smaller bite-sized subproblems. The idea behind this is that those problems are hard to solve due to their complexity. To make it easier, you can divide these problems into smaller problems. Solving those smaller bits will make it easier to solve the larger problem in the long run.
2. Increase Cohesion
Cohesion means grouping things that make sense together — sort of as one package. From a development point of view, you can choose to design your packages, modules, or classes cohesively.Cohesion brings about the organization of your code, and it will make it much easier to find things, thus simplifying the system.
3. Design for Flexibility
Designing for flexibility comes down to anticipating changes to your system in the future. Your system may be simple in the present but get more complex in the future. You may want to add a lot more stuff. You may want to swap out an implementation of an object or an item for a better one. A lot of times, people design systems for today’s use. They don’t think about the fact that in a month or maybe in a year, they’re going to scale the project up.
4. Design for Portability
When designing a system, you need to remember that it may be used on a different platform or device than what you’re currently targeting. If you are making a web application just for the web, it will be costly and time-consuming if you ever want to turn this into an iOS app, an Android app, a Windows desktop application, or something like that. That may involve creating an entirely new system to be able to port.
Q3.Write a short note on the following:
Answer:
a) Black Box Testing: Black Box Testing is a software testing method in which the functionalities of software applications are tested without having knowledge of internal code structure, implementation details and internal paths. Black Box Testing mainly focuses on input and output of software applications and it is entirely based on software requirements and specifications. It is also known as Behavioral Testing.
There are the generic steps followed to carry out any type of Black Box Testing.
b) White Box Testing:
White Box Testing is software testing technique in which internal structure, design and coding of software are tested to verify flow of input-output and to improve design, usability and security. In white box testing, code is visible to testers so it is also called Clear box testing, Open box testing, Transparent box testing, Code-based testing and Glass box testing.
It is one of two parts of the Box Testing approach to software testing. Its counterpart, Blackbox testing, involves testing from an external or end-user type perspective. On the other hand, Whitebox testing is based on the inner workings of an application and revolves around internal testing.
Working process of white box testing:
Input: Requirements, Functional specifications, design documents, source code.
Processing: Performing risk analysis for guiding through the entire process.
Proper test planning: Designing test cases so as to cover entire code. Execute rinse-repeat until error-free software is reached. Also, the results are communicated.
Output: Preparing final report of the entire testing process.
Testing techniques:
Statement coverage: In this technique, the aim is to traverse all statement at least once. Hence, each line of code is tested. In case of a flowchart, every node must be traversed at least once. Since all lines of code are covered, helps in pointing out faulty code.
Branch Coverge: In this technique, test cases are designed so that each branch from all decision points are traversed at least once. In a flowchart, all edges must be traversed at least once.
See lessThe memory address of the first element of an array is called?
Correct option to the question 'The memory address of the first element of an array is called' is D. base address
Correct option to the question ‘The memory address of the first element of an array is called’ is D. base address
See less